Cognitive training can boost and sharpen the brain’s abilities to remember, focus,
and switch between different tasks. One of the key elements of cognitive training is
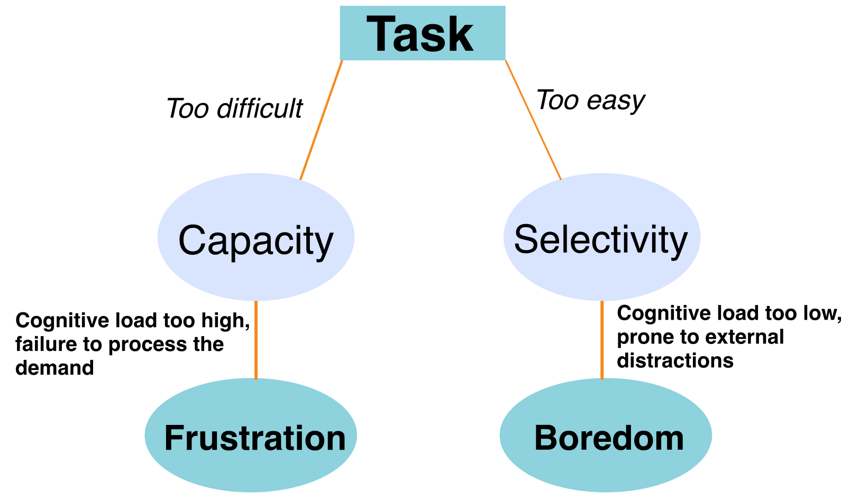
that it manipulates 'cognitive load', by adjusting the intensity of the intervention
to suit the participant’s ability level and keep the session enjoyable. This study
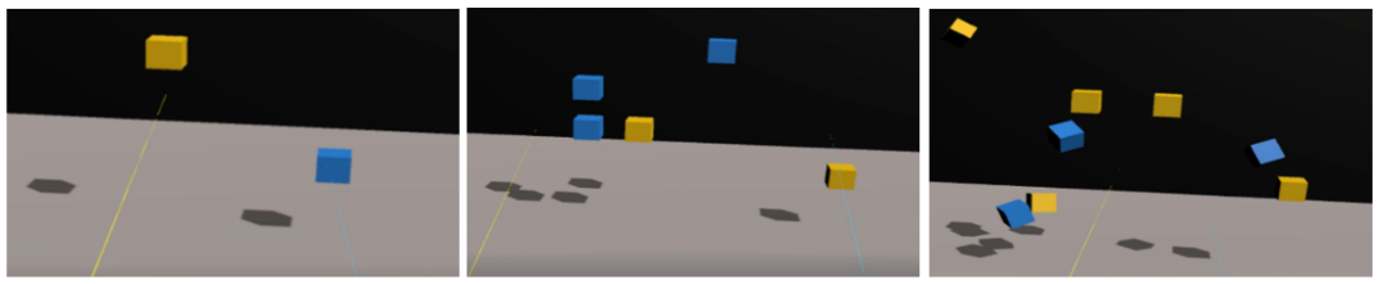
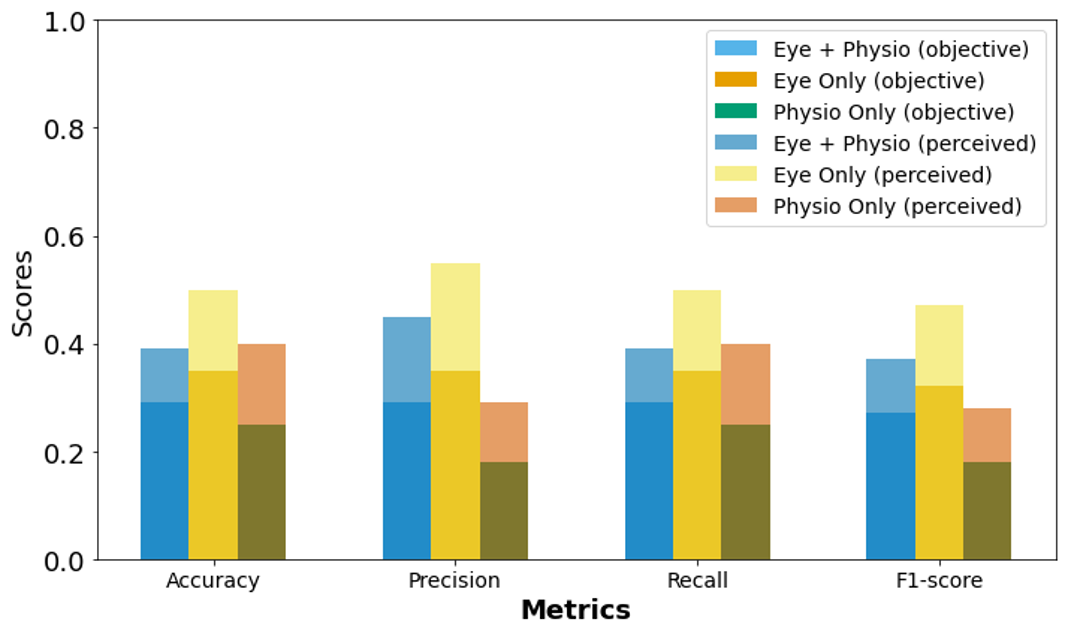
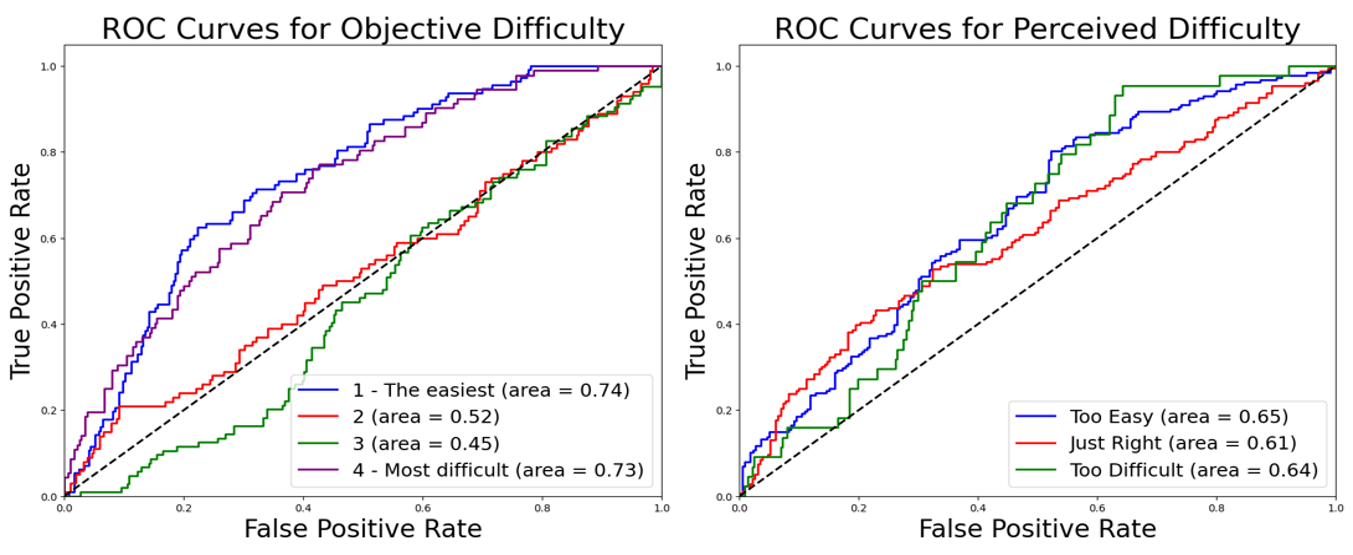
introduces a novel sustained attention task in Virtual Reality (VR) to predict cognitive load dynamically.
Unlike previous research, which often used non-VR settings, simpler tasks, or performance metrics as
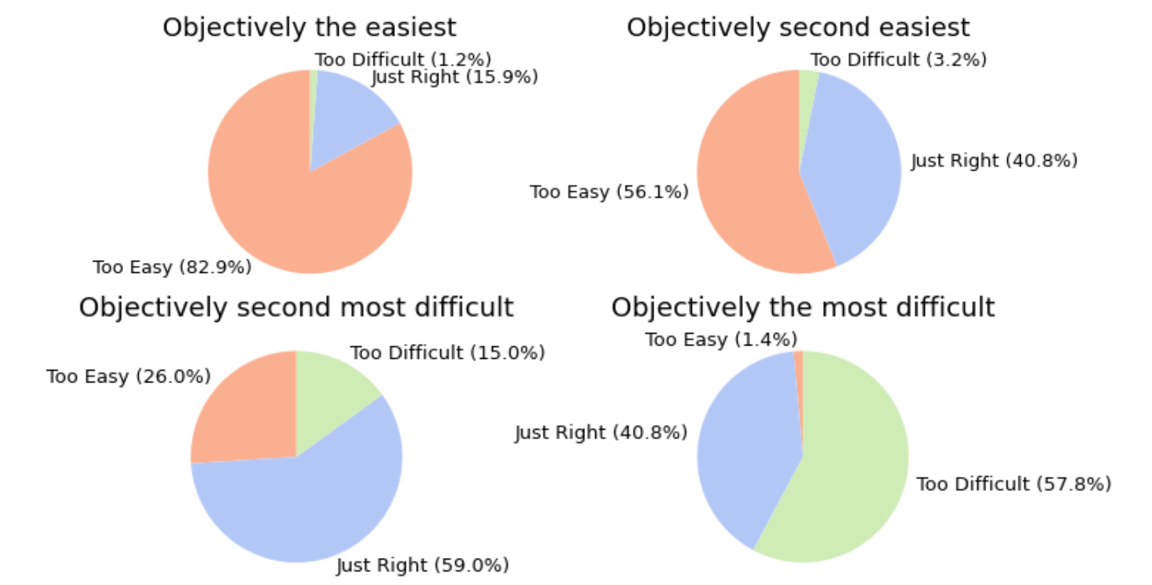
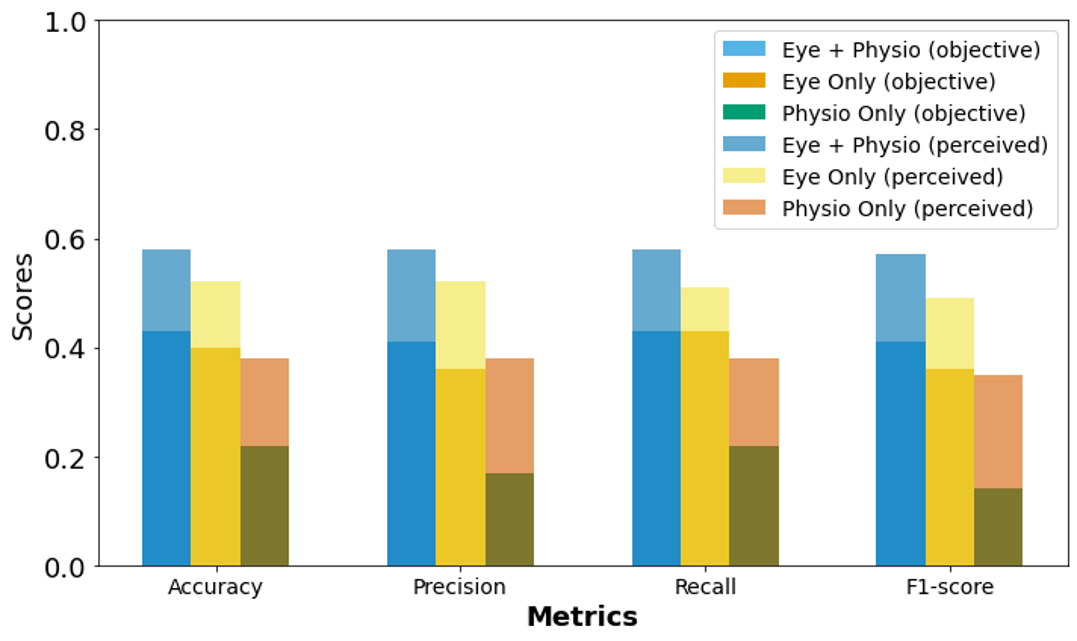
predictors, our approach aims to measure cognitive load objectively in a more ecologically valid and
gamified VR environment. We employed machine learning techniques to enable real-time, personalized cognitive training.
This work contributes to the development of more effective cognitive training interventions that can adapt to
individual differences and maintain optimal engagement levels.